Does BMW own Volkswagen? This intriguing question sets the stage for an exploration into the ownership structures and historical connections between two of the world’s leading automotive manufacturers. From their humble beginnings to their current positions as industry titans, BMW and Volkswagen have charted distinct paths while occasionally crossing paths in the competitive automotive landscape.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of BMW’s and Volkswagen’s ownership structures, examining their subsidiaries, brands, and the individuals or entities that hold the reins of power. We will also trace the historical relationship between these two companies, highlighting key collaborations and milestones that have shaped their interactions.
Company Ownership
BMW, an abbreviation for Bayerische Motoren Werke AG, is a German multinational company that produces luxury vehicles and motorcycles. BMW’s current ownership structure is the result of a long and complex history involving various mergers, acquisitions, and investments.
Initially, BMW was founded in 1916 as a manufacturer of aircraft engines. After World War I, the company diversified into producing motorcycles and automobiles. Over the years, BMW has acquired several other companies, including Rolls-Royce Motor Cars in 1998 and Mini in 2000.
BMW and Volkswagen are two distinct automotive giants. While BMW is known for its luxury vehicles, Volkswagen focuses on producing more affordable cars. However, many car enthusiasts often wonder about the connection between these two brands. Do BMW take premium gas? The answer is yes, as BMW vehicles are designed to perform optimally with high-octane fuel.
Click here to learn more about the benefits of using premium gas in your BMW. Returning to our initial topic, BMW and Volkswagen remain separate entities, each with its own unique strengths and target markets.
Shareholders
- Stefan Quandt (29.9%)
- Susanne Klatten (21.0%)
- Public float (50.1%)
Currently, the majority of BMW’s shares are owned by the Quandt family, descendants of the company’s founders. Stefan Quandt and Susanne Klatten, the children of Herbert Quandt, control a combined 50.9% of the company’s shares through their holding company, SKion GmbH.
Board of Management
- Oliver Zipse (CEO)
- Pieter Nota (Member of the Board of Management responsible for Customer, Brands and Sales)
- Nicolas Peter (Member of the Board of Management responsible for Finance)
- Milan Nedeljković (Member of the Board of Management responsible for Production)
- Frank Weber (Member of the Board of Management responsible for Development)
The day-to-day operations of BMW are managed by the Board of Management, which is appointed by the Supervisory Board. The Supervisory Board, in turn, is elected by the shareholders at the company’s annual general meeting.
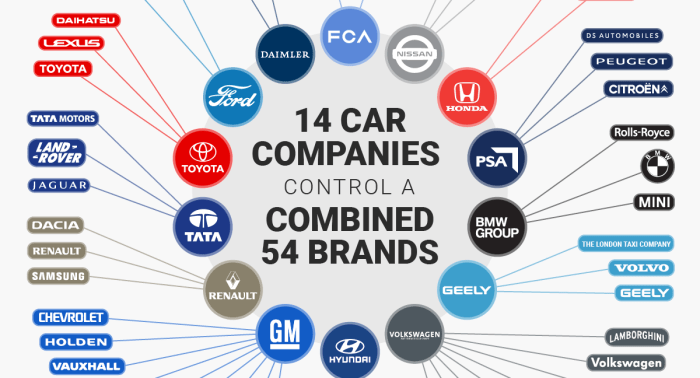
Volkswagen Group Structure
Volkswagen Group is a multinational automotive manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Wolfsburg, Germany. It is the world’s second-largest automaker by production and revenue, behind Toyota. The group’s corporate structure is complex, with numerous subsidiaries and brands.
Contrary to popular belief, BMW does not own Volkswagen. However, if you’re curious about BMW’s reliability, you can find out more about are bmw reliable . BMW is known for its high-performance vehicles, but reliability is a different matter. Researching before making a decision is always wise, especially when it comes to big purchases like cars.
Volkswagen Group is owned by a consortium of investors, including the Porsche and Piëch families, the German state of Lower Saxony, and the Qatar Investment Authority. The group’s management board is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the company, while the supervisory board oversees the management board and represents the interests of the shareholders.
Subsidiaries and Brands
Volkswagen Group has a wide range of subsidiaries and brands, including:
- Volkswagen: The core brand of the group, producing a wide range of passenger cars.
- Audi: A luxury car brand known for its high-performance vehicles.
- Bentley: A British luxury car brand known for its handcrafted vehicles.
- Bugatti: A French luxury car brand known for its hypercars.
- Lamborghini: An Italian luxury car brand known for its exotic sports cars.
- Porsche: A German luxury car brand known for its sports cars and SUVs.
- SEAT: A Spanish car brand known for its affordable and sporty vehicles.
- Škoda: A Czech car brand known for its value-for-money vehicles.
- MAN: A German commercial vehicle brand known for its trucks and buses.
- Scania: A Swedish commercial vehicle brand known for its trucks and buses.
- Traton: A holding company for Volkswagen Group’s commercial vehicle brands.
These subsidiaries and brands operate independently, but they share resources and technologies within the Volkswagen Group.
BMW doesn’t own Volkswagen, but it does have a partnership with Rolls-Royce. Does BMW own Rolls-Royce ? The answer is yes, BMW Group acquired Rolls-Royce Motor Cars in 1998. Back to the topic of BMW and Volkswagen, their partnership involves sharing technology and platforms, but they remain separate companies.
Historical Relationship: Does Bmw Own Volkswagen
BMW and Volkswagen have had a complex and evolving relationship over the years. While they have not been directly affiliated, they have engaged in collaborations and partnerships, as well as experienced periods of competition and rivalry.
Unlike Volkswagen, which is owned by the Volkswagen Group, BMW remains an independent automaker. However, if you’re curious about the reliability of a specific BMW model, such as the 3 Series, you can check out this article: are bmw 3 series reliable . It provides valuable insights into the dependability of this popular luxury sedan.
While BMW and Volkswagen may have different ownership structures, they both offer a range of vehicles with varying levels of reliability.
Early Collaborations
In the 1970s, BMW and Volkswagen collaborated on the development of the Golf GTI, a high-performance hatchback that became a popular success. This collaboration laid the foundation for future joint projects and established a level of mutual respect between the two companies.
Audi Acquisition
In 1964, Volkswagen acquired a majority stake in Audi, a German automaker known for its luxury and performance vehicles. This acquisition brought Audi under the Volkswagen Group umbrella, creating a formidable competitor to BMW in the premium car market.
Competition and Rivalry
Despite their collaborations, BMW and Volkswagen have also been fierce competitors, particularly in the luxury car segment. Each company has strived to outdo the other in terms of performance, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
Recent Developments
In recent years, BMW and Volkswagen have continued to compete in the automotive market, while also exploring opportunities for cooperation. In 2019, the two companies announced a joint venture to develop and produce electric vehicles, signaling a potential shift towards collaboration in the face of industry-wide challenges.
Market Competition
BMW and Volkswagen are two of the world’s leading automakers, with a significant presence in the global automotive market. They compete directly in several segments, including luxury cars, SUVs, and electric vehicles.
In terms of market share, Volkswagen has a slight edge over BMW. In 2022, Volkswagen sold 8.3 million vehicles worldwide, while BMW sold 2.5 million vehicles.
Product Offerings
Both BMW and Volkswagen offer a wide range of vehicles, from compact cars to luxury sedans and SUVs. BMW is known for its high-performance vehicles, while Volkswagen is known for its more affordable and practical vehicles.
Target Customer Base
BMW and Volkswagen target different customer bases. BMW targets affluent consumers who are looking for high-performance and luxury vehicles. Volkswagen targets a broader range of consumers, including families and budget-conscious buyers.
Financial Performance
BMW and Volkswagen are two of the world’s largest automakers, and their financial performance is closely watched by investors and analysts. Both companies have been profitable in recent years, but there are some key differences in their financial profiles.
One of the most striking differences between BMW and Volkswagen is their revenue. In 2021, BMW generated €111.24 billion in revenue, while Volkswagen generated €250.2 billion. This difference is largely due to the fact that Volkswagen sells a wider range of vehicles, including passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and motorcycles.
Another key difference between BMW and Volkswagen is their profitability. In 2021, BMW’s operating profit margin was 9.8%, while Volkswagen’s operating profit margin was 7.7%. This difference is due to a number of factors, including BMW’s focus on higher-margin luxury vehicles and Volkswagen’s exposure to the more competitive mass market.
BMW and Volkswagen are two separate automakers, so BMW does not own Volkswagen. However, if you’re curious about whether BMWs have remote start capabilities, you can check out this informative article: do bmw have remote start . Regardless, BMW and Volkswagen remain distinct entities in the automotive industry.
Revenue
- BMW: €111.24 billion (2021)
- Volkswagen: €250.2 billion (2021)
BMW’s revenue is primarily generated from the sale of passenger cars and motorcycles. Volkswagen’s revenue is more diversified, with a significant portion coming from the sale of commercial vehicles and motorcycles.
Profitability, Does bmw own volkswagen
- BMW: 9.8% operating profit margin (2021)
- Volkswagen: 7.7% operating profit margin (2021)
BMW’s higher profitability is due to its focus on higher-margin luxury vehicles. Volkswagen’s profitability is lower due to its exposure to the more competitive mass market.
Industry Outlook
The automotive industry is poised for significant transformation in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and environmental concerns. These trends present both opportunities and challenges for automakers like BMW and Volkswagen.
Technological Advancements
Autonomous driving, electric vehicles (EVs), and connected cars are revolutionizing the industry. These technologies enhance safety, reduce emissions, and improve convenience for consumers. BMW and Volkswagen have invested heavily in these areas to stay competitive and meet evolving customer demands.
End of Discussion
The relationship between BMW and Volkswagen is a complex tapestry woven from a blend of competition, cooperation, and mutual respect. While they are formidable rivals in the marketplace, they have also found common ground in addressing industry challenges and driving innovation.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve at a rapid pace, it remains to be seen how the dynamics between BMW and Volkswagen will unfold in the years to come.