Unveiling the Yamaha R6 Engine Diagram: A Comprehensive Exploration into the Heart of a Racing Legend. Immerse yourself in the intricate details of this high-performance engine, deciphering its design, components, and the symphony of its performance.
From the meticulously engineered cylinder head to the symphony of the exhaust system, this guide unveils the secrets behind the R6’s exhilarating power and efficiency.
Yamaha R6 Engine Overview
The Yamaha R6 engine is a 599cc, liquid-cooled, inline-four engine that produces 118 horsepower at 14,500 rpm and 61.7 lb-ft of torque at 10,500 rpm. It has a bore and stroke of 67.0 mm x 42.5 mm and a compression ratio of 13.1:1. The engine is equipped with a DOHC valve train with four valves per cylinder.The
R6 engine is known for its high-revving nature and screaming exhaust note. It is also relatively fuel-efficient, getting up to 40 mpg in real-world riding conditions.
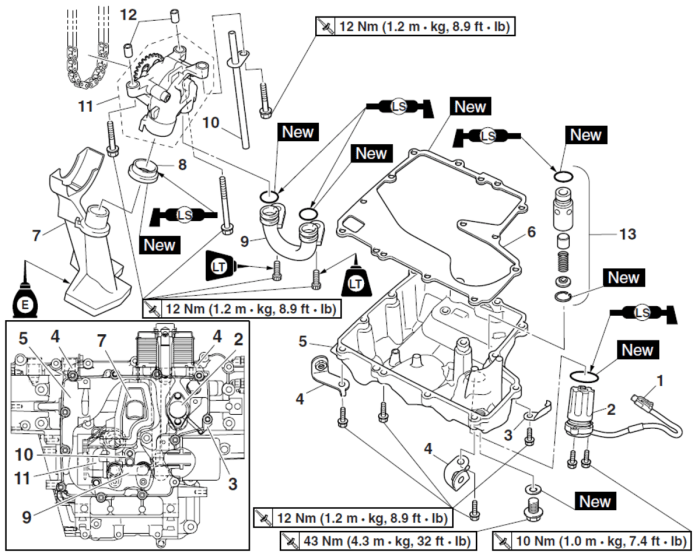
Engine Components: Yamaha R6 Engine Diagram
The Yamaha R6 engine is a masterpiece of engineering, meticulously designed to deliver an exhilarating riding experience. It’s a symphony of precision-crafted components working harmoniously to unleash raw power and responsiveness.
Understanding the intricate workings of the Yamaha R6 engine diagram is crucial for enthusiasts seeking to optimize their machines. By studying the diagram, you can identify potential upgrades and modifications. If you’re eager to enhance the performance and aesthetics of your R6, explore the wide range of yamaha r6 aftermarket parts available.
From exhaust systems to bodywork, these components can transform your R6 into a true head-turner. Once you’ve selected the perfect upgrades, revisiting the engine diagram will help you visualize the installation process and ensure a seamless integration.
In this section, we’ll delve into the intricate details of these key engine components, exploring their functions and how they contribute to the R6’s legendary performance.
Cylinder Head, Yamaha r6 engine diagram
The cylinder head is the brain of the engine, housing the valves, camshafts, and spark plugs. Its primary role is to control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and exhaust gases out of them.
Pistons and Connecting Rods
Pistons are cylindrical components that move up and down within the cylinders. They receive the force from the combustion process and transfer it to the crankshaft via connecting rods.
Yamaha R6’s engine is an inline-four cylinder, liquid-cooled, four-stroke engine that produces 118.4 horsepower and 52.4 lb-ft of torque. The engine is paired with a six-speed transmission. For more information on the Yamaha R6, check out this page: yamaha r6 bike . The Yamaha R6 engine diagram shows the detailed layout of the engine, including the location of the cylinders, pistons, crankshaft, and other components.
Camshaft and Timing Chain
The camshaft is a crucial component that controls the timing of the valves. It opens and closes the valves at precise moments to ensure optimal engine performance. The timing chain connects the camshaft to the crankshaft, synchronizing their movements.
Oil Pump and Lubrication System
The oil pump ensures that all moving parts of the engine are adequately lubricated. It circulates oil throughout the engine, reducing friction and wear, and maintaining optimal engine health.
Intake and Exhaust Systems
The Yamaha R6’s intake and exhaust systems play a crucial role in optimizing engine performance. These systems are meticulously designed to ensure efficient air-fuel mixture delivery and effective exhaust gas removal.
The intake system consists of a fuel injection system and throttle bodies. The fuel injection system precisely delivers fuel into the engine’s cylinders, ensuring an optimal air-fuel ratio for combustion. The throttle bodies control the airflow into the engine, adjusting the mixture based on the rider’s throttle input.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system comprises headers, a catalytic converter, and a muffler. The headers collect exhaust gases from the cylinders and direct them into the catalytic converter. The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances. The muffler dampens the exhaust noise, ensuring compliance with noise regulations.
Engine Management System
The engine management system (EMS) is the brain of the Yamaha R6 engine, controlling various aspects of its performance to optimize power, efficiency, and emissions. It consists of a series of sensors, actuators, and a computer that analyzes data and adjusts engine parameters accordingly.
If you’re keen on learning more about the intricate details of the Yamaha R6 engine, studying its diagram is a great place to start. For those curious about the engine’s cubic capacity, you can find comprehensive information on the Yamaha R6 cc . Returning to the engine diagram, it provides a visual representation of the engine’s components and their interconnections, helping you understand its inner workings.
Sensors
The EMS relies on a network of sensors to monitor engine conditions. These sensors include:
- Throttle position sensor (TPS): Measures the position of the throttle valve.
- Intake air temperature sensor (IAT): Measures the temperature of the air entering the engine.
- Coolant temperature sensor (CTS): Measures the temperature of the engine coolant.
- Oxygen sensor (O2 sensor): Measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases.
Actuators
The EMS uses actuators to adjust engine parameters based on sensor data. These actuators include:
- Fuel injectors: Control the amount of fuel injected into the engine.
- Ignition coils: Control the timing and intensity of the spark plugs.
- Variable valve timing (VVT) system: Adjusts the timing of the intake and exhaust valves.
Engine Maps
The EMS stores a series of engine maps that define how the engine should behave under different operating conditions. These maps include:
- Fuel map: Controls the amount of fuel injected at different engine speeds and loads.
- Ignition map: Controls the timing and intensity of the spark plugs at different engine speeds and loads.
- VVT map: Controls the timing of the intake and exhaust valves at different engine speeds and loads.
By adjusting these maps, the EMS can optimize engine performance for different riding conditions, such as acceleration, cruising, and fuel economy.
Performance Characteristics
The Yamaha R6 engine delivers an impressive performance that sets it apart in its class. With its advanced engineering and design, it offers a thrilling and exhilarating riding experience.
The following table summarizes the key performance characteristics of the Yamaha R6 engine:
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Horsepower | 118.4 hp @ 14,500 rpm |
| Torque | 61.7 ft-lb @ 10,500 rpm |
| Fuel Efficiency | 40 mpg (city) / 50 mpg (highway) |
Compared to other engines in its class, the Yamaha R6 engine stands out with its exceptional horsepower and torque output. It delivers a smooth and responsive power delivery throughout the rev range, providing riders with a thrilling and engaging ride.
Summary
In conclusion, the Yamaha R6 engine diagram unveils a masterpiece of engineering, meticulously crafted to deliver an exhilarating symphony of power and precision. Its intricate components and advanced systems orchestrate a harmonious performance that sets the R6 apart as a true icon in the world of motorcycling.
