Do Subarus have timing belts? This question has puzzled many Subaru owners and enthusiasts alike. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of Subaru engines, timing belts, and their implications, providing you with a clear understanding of this crucial component and its role in your Subaru’s performance.
From exploring the different types of Subaru engines to understanding the advantages and disadvantages of timing belts versus timing chains, we cover every aspect of this topic. We’ll also discuss the maintenance schedule for timing belt replacement and the potential consequences of timing belt failure.
So, buckle up and join us on this informative journey into the world of Subaru timing belts.
Overview of Subaru Engines
Subaru vehicles are renowned for their reliability and performance, which is partly attributed to the exceptional engines they utilize. Subaru offers a diverse range of engines, each meticulously engineered to deliver a unique driving experience. In this section, we will explore the various types of engines employed in Subaru vehicles, providing a comprehensive overview of their configurations and capabilities.
Engine Types
Subaru utilizes a variety of engine configurations to cater to different performance and fuel efficiency requirements. These engines can be broadly classified into two main categories: naturally aspirated and turbocharged.
- Naturally Aspirated Engines:These engines rely solely on atmospheric pressure to fill their cylinders with air. They are typically characterized by their smooth power delivery and linear torque curve.
- Turbocharged Engines:Turbochargers are employed to force more air into the cylinders, resulting in increased power and torque. Turbocharged engines offer impressive performance but may exhibit some turbo lag at low engine speeds.
Engine Configurations
Subaru engines come in a variety of configurations, including flat-four, flat-six, and V-type engines. Each configuration offers distinct advantages and disadvantages.
- Flat-Four Engines:Subaru’s signature flat-four engine is known for its compact size, low center of gravity, and balanced operation. It is a popular choice for many Subaru models due to its efficiency and reliability.
- Flat-Six Engines:Flat-six engines provide a smoother power delivery and increased torque compared to flat-four engines. They are typically found in higher-performance Subaru models.
- V-Type Engines:V-type engines are characterized by their V-shaped cylinder arrangement. They are typically found in larger Subaru vehicles and offer a combination of power and fuel efficiency.
Engine Displacement
Subaru engines come in a range of displacements, from 1.6 liters to 3.6 liters. The displacement of an engine refers to the total volume of its cylinders. Larger displacement engines generally produce more power and torque, but they also tend to be less fuel-efficient.
If you’re curious about whether Subarus have timing belts, you’re in the right place. Subarus use timing chains instead of timing belts. Unlike belts, timing chains generally last the lifetime of the engine. If you’re interested in flat towing your Subaru, check out this article for more information.
It’s important to note that flat towing a Subaru with a continuously variable transmission (CVT) is not recommended. For vehicles with a manual transmission, it’s crucial to put the transmission in neutral and disconnect the driveshaft before flat towing.
| Engine Type | Configuration | Displacement (liters) |
|---|---|---|
| Naturally Aspirated | Flat-Four | 1.6, 2.0, 2.5 |
| Turbocharged | Flat-Four | 2.0, 2.4, 2.5 |
| Naturally Aspirated | Flat-Six | 3.0, 3.6 |
| Turbocharged | V-Type | 3.0, 3.6 |
Timing Belts vs. Timing Chains
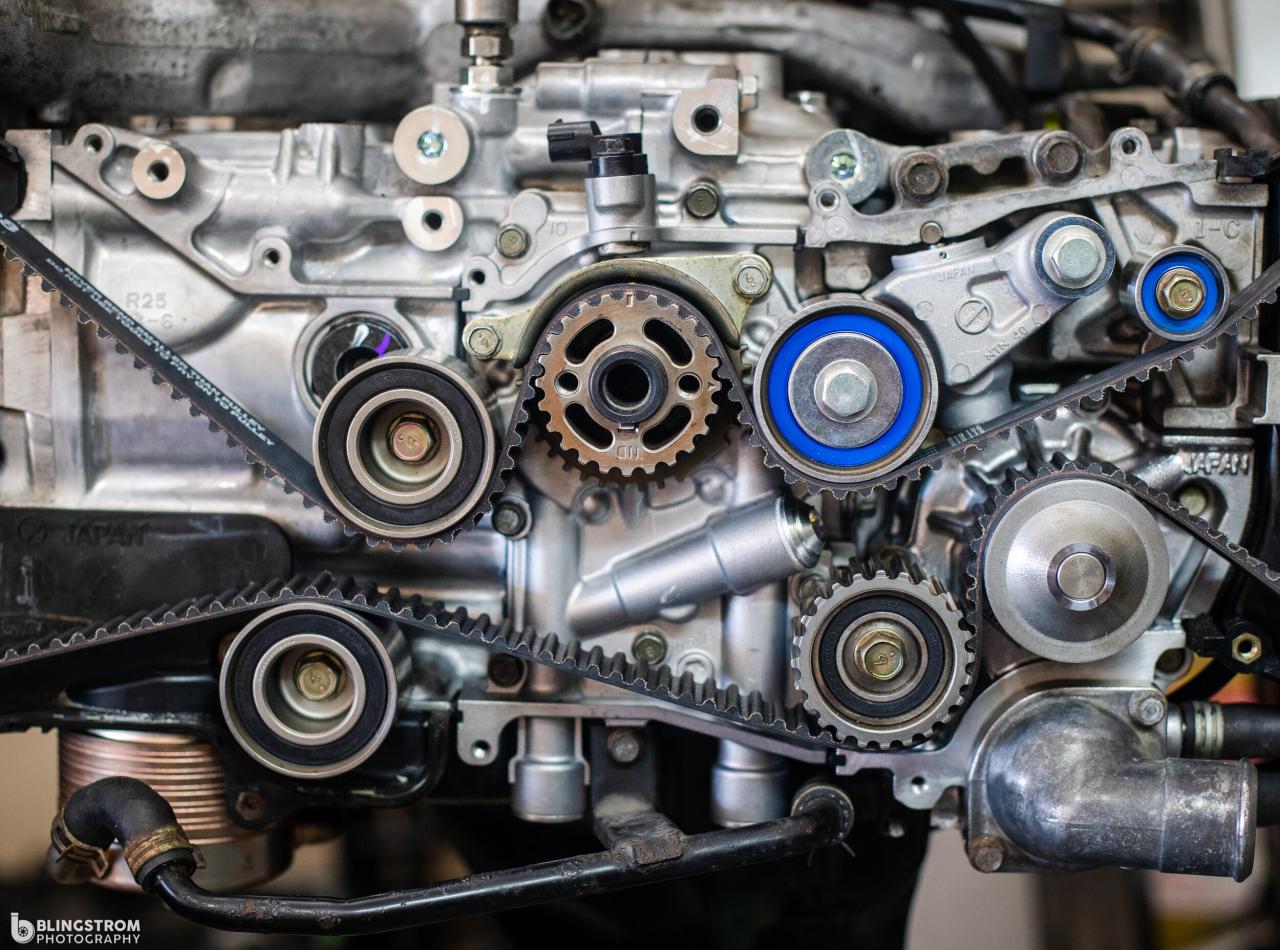
In internal combustion engines, timing belts and timing chains are critical components responsible for synchronizing the movement of the crankshaft and camshaft. Understanding their differences is essential for engine maintenance and performance.
While Subarus don’t have timing belts, they’re known for their exceptional performance in snowy conditions. With their symmetrical all-wheel drive system, Subarus offer superior traction and stability on slippery roads. To learn more about their snow prowess, check out our article on are Subarus good in snow . Getting back to the topic of timing belts, Subarus use timing chains instead, which are generally more durable and require less maintenance than belts.
Timing Belts, Do subarus have timing belts
Timing belts are flexible, toothed belts made of reinforced rubber or polyurethane. They connect the crankshaft to the camshaft, ensuring that the valves open and close at the appropriate times relative to the piston movement.
Timing Chains
Timing chains are made of metal links and resemble bicycle chains. They also connect the crankshaft to the camshaft, providing a more durable and longer-lasting alternative to timing belts.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Timing Belts
- Quieter operation
- Lower initial cost
- Easier to replace
- Shorter lifespan (typically 60,000-100,000 miles)
- Can fail catastrophically if not replaced on time
Timing Chains
- Longer lifespan (typically 150,000-200,000 miles)
- More durable and reliable
- No catastrophic failure risk
- Noisier operation
- Higher initial cost
- More difficult to replace
Subaru’s Use of Timing Belts
Subaru utilizes timing belts in specific models within its lineup. These belts play a crucial role in synchronizing the timing of the engine’s valves and crankshaft, ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity.
Models Using Timing Belts
Subaru models that employ timing belts include:
- Impreza (non-WRX/STI)
- Legacy
- Outback
- Forester
- Crosstrek
- Ascent
Reasons for Using Timing Belts
Subaru opts for timing belts in these models primarily due to cost and noise reduction. Timing belts are generally less expensive to produce and replace compared to timing chains. Additionally, they operate more quietly, contributing to a quieter overall engine operation.
Maintenance Schedule
The maintenance schedule for timing belt replacement in Subaru vehicles varies depending on the specific model and year. However, as a general guideline, Subaru recommends replacing the timing belt every 60,000 to 105,000 miles (97,000 to 170,000 kilometers) or 6 to 8 years, whichever comes first.
Neglecting to replace the timing belt within the recommended interval can result in catastrophic engine damage if the belt fails. Therefore, it is crucial to adhere to the maintenance schedule and have the timing belt inspected and replaced as necessary.
Consequences of Timing Belt Failure: Do Subarus Have Timing Belts
Timing belt failure can lead to catastrophic engine damage. When the timing belt breaks, the crankshaft and camshaft will no longer be synchronized, and the pistons will collide with the valves. This can cause severe damage to the pistons, valves, and cylinder head.
There are several signs and symptoms that can indicate a failing timing belt. These include:
- A squealing or chirping noise from the engine
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Reduced engine power
- Increased fuel consumption
It is important to have the timing belt replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule. Failure to do so can lead to costly engine repairs.
Wondering if Subarus have timing belts? The answer is yes, most Subaru models do have timing belts. These belts help keep the engine’s timing in sync, ensuring optimal performance. Speaking of performance, if you’re curious about how Subarus handle in snowy conditions, check out this article on whether the Subaru Crosstrek can drive in snow: can subaru crosstrek drive in snow . It provides valuable insights into the Crosstrek’s capabilities in snowy environments.
Returning to our original topic, timing belts are an essential component of Subaru engines, contributing to their reliability and durability.
Alternative Timing Belt Options
Subaru vehicles typically use timing belts, but there are alternative options available in the market. These alternatives offer advantages and disadvantages compared to the original equipment timing belts.
One alternative is to use aftermarket timing belts. These belts are manufactured by companies other than Subaru and are often priced lower than the original equipment belts. However, it is important to choose aftermarket timing belts carefully, as some may not be as durable or reliable as the original equipment belts.
Choosing the Right Timing Belt
When choosing a timing belt for your Subaru, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The age and mileage of your vehicle
- The type of driving you do
- The climate in which you live
If you have a newer Subaru with low mileage, you may be able to get away with using an aftermarket timing belt. However, if you have an older Subaru with high mileage, it is best to stick with the original equipment timing belt.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of timing belts in Subaru vehicles is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Whether you’re a seasoned Subaru owner or a prospective buyer, this guide has provided you with a comprehensive overview of timing belts, their significance, and the implications of their failure.
Remember, timely maintenance and the use of high-quality timing belts are crucial for a trouble-free driving experience. So, stay informed, stay proactive, and keep your Subaru running smoothly for miles to come.